The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is one of the most frustrating errors Windows users can encounter. It appears when your system encounters a critical error it cannot recover from, forcing your computer to shut down abruptly. If you’re using Windows 11 and facing this issue, don’t panic! In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to fix the Blue Screen of Death on Windows 11.
Contents
What is the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)?
The Blue Screen of Death is a stop error screen displayed by Windows when it encounters a critical system error. It usually appears with a cryptic error message, such as:
- CRITICAL_PROCESS_DIED
- SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED
- IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
- PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA
These errors can be caused by hardware issues, faulty drivers, corrupted system files, or software conflicts.
Common Causes of Blue Screen of Death in Windows 11
Before diving into the fixes, it’s important to understand what might be causing the BSOD. Here are some common culprits:
- Outdated or Corrupted Drivers: Faulty drivers are a leading cause of BSOD errors.
- Hardware Issues: Problems with RAM, hard drives, or other hardware components can trigger BSOD.
- Corrupted System Files: Missing or corrupted Windows system files can cause instability.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible or poorly coded software can lead to crashes.
- Overheating: If your system overheats, it may shut down to prevent damage.
- Windows Updates: Sometimes, a recent update can cause compatibility issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix Blue Screen of Death on Windows 11
Follow these steps to troubleshoot and fix the BSOD error on your Windows 11 PC.
Step 1: Note the Error Code
When the BSOD appears, it will display an error code (e.g., CRITICAL_PROCESS_DIED). Write this down, as it can help you identify the root cause of the problem.
Step 2: Restart Your Computer
Sometimes, the BSOD is a one-time glitch. Restart your computer and see if the issue persists. If the error recurs, proceed to the next steps.
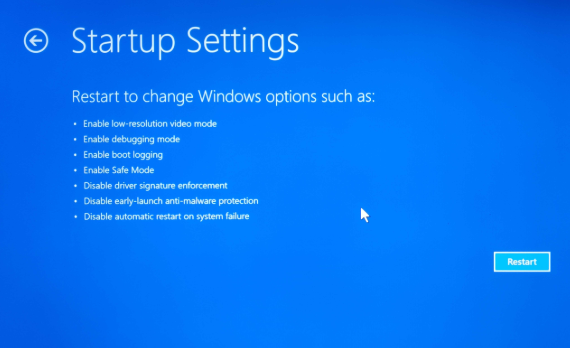
Step 3: Boot into Safe Mode
Safe Mode starts Windows with only the essential drivers and services, which can help you troubleshoot the issue.
- Press
Windows + Ito open Settings. - Go to System > Recovery.
- Under Advanced Startup, click Restart Now.
- After your PC restarts, select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Press F4 to boot into Safe Mode.
Step 4: Uninstall Recent Updates or Software
If the BSOD started after a recent update or software installation, it might be the culprit.
- Uninstall Updates:
- Go to Settings > Windows Update > Update History.
- Click Uninstall Updates and remove the most recent update.
- Uninstall Software:
- Go to Control Panel > Programs > Uninstall a Program.
- Remove any recently installed software.
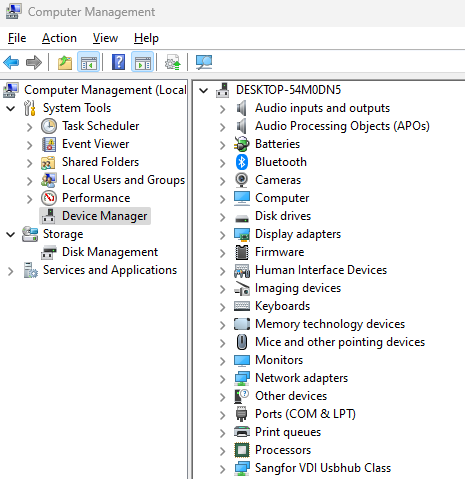
Step 5: Update or Roll Back Drivers
Faulty drivers are a common cause of BSOD errors. Here’s how to update or roll back drivers:
- Press
Windows + Xand select Device Manager. - Expand the categories and look for devices with a yellow exclamation mark.
- Right-click the device and select Update Driver.
- If the issue started after a driver update, select Roll Back Driver instead.
Step 6: Run a System File Checker (SFC) Scan
Corrupted system files can cause BSOD errors. Use the System File Checker tool to repair them.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
sfc /scannow
- Wait for the scan to complete. If any issues are found, the tool will attempt to fix them.
Step 7: Run a DISM Scan
The Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM) can repair the Windows image.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type the following commands one by one, pressing Enter after each:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- Restart your computer after the process completes.
Step 8: Check for Memory Issues
Faulty RAM can cause BSOD errors. Use the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool to check for memory issues.
- Press
Windows + R, type mdsched.exe, and press Enter. - Select Restart now and check for problems.
- Your PC will restart and run the memory test. If any issues are found, consider replacing your RAM.
Step 9: Check for Disk Errors
Hard drive issues can also cause BSOD errors. Use the CHKDSK tool to check for disk errors.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
chkdsk /f /r
- Restart your computer to allow the tool to scan and repair your disk.
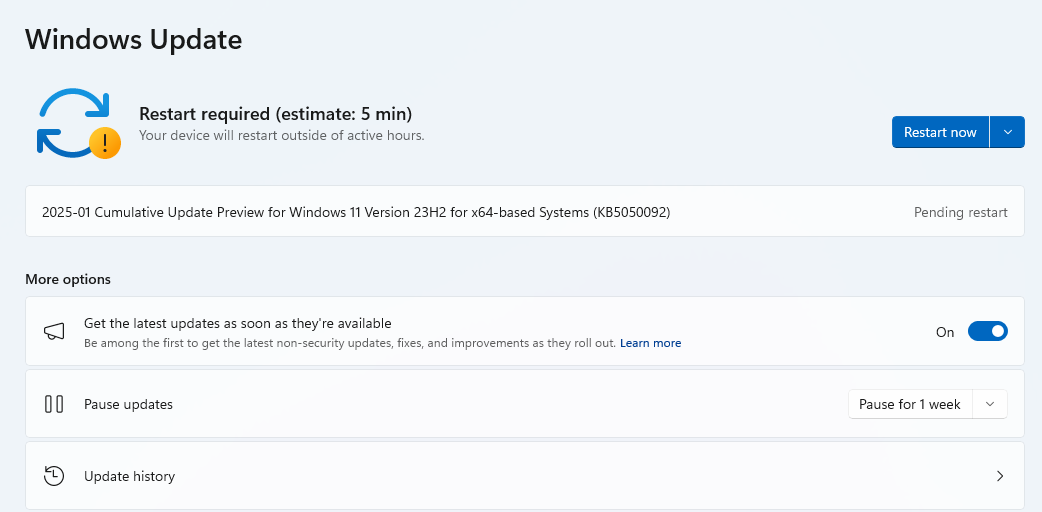
Step 10: Update Windows
Ensure your Windows 11 is up to date, as updates often include bug fixes and patches.
- Go to Settings > Windows Update.
- Click Check for Updates and install any available updates.
Step 11: Perform a Clean Boot
A clean boot starts Windows with minimal drivers and startup programs, helping you identify software conflicts.
- Press
Windows + R, type msconfig, and press Enter. - Go to the Services tab, check Hide all Microsoft services, and click Disable all.
- Go to the Startup tab and click Open Task Manager.
- Disable all startup items.
- Restart your computer and check if the BSOD persists.
Step 12: Reset or Reinstall Windows
If none of the above steps work, you may need to reset or reinstall Windows.
- Go to Settings > System > Recovery.
- Click Reset PC and choose Keep my files or Remove everything.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
Preventing Blue Screen of Death in the Future
Here are some tips to avoid BSOD errors in the future:
- Keep Windows Updated: Regularly install Windows updates.
- Update Drivers: Ensure all your drivers are up to date.
- Use Reliable Software: Avoid installing untrusted or incompatible software.
- Monitor Hardware: Keep an eye on your hardware health, especially RAM and hard drives.
- Avoid Overheating: Ensure your PC has proper ventilation and cooling.
Conclusion
The Blue Screen of Death can be intimidating, but with the right troubleshooting steps, you can fix it and get your Windows 11 PC back to normal. Start by identifying the error code, then follow the steps outlined in this guide to resolve the issue. If all else fails, resetting or reinstalling Windows may be your best option.
By following these tips and maintaining your system, you can minimize the chances of encountering Fix Blue Screen (BSOD) errors in the future. If you found this guide helpful, share it with others who might be facing the same issue!